Road Safety Management
The outer layer of the Safe System Approach addresses Road Safety Management, which is essential for the successful implementation and sustainability of road safety strategies.
On this page, you will find a brief overview of the components that make up the outer layer of the Safe System, including leadership, target setting, funding, legislation, coordination, promotion, monitoring and evaluation, research and development (R&D), and knowledge transfer. You will also learn about the implementation gap, which bridges the outer layer with the inner circle containing the core principles, ensuring that road safety measures are effectively applied and continuously enhanced.
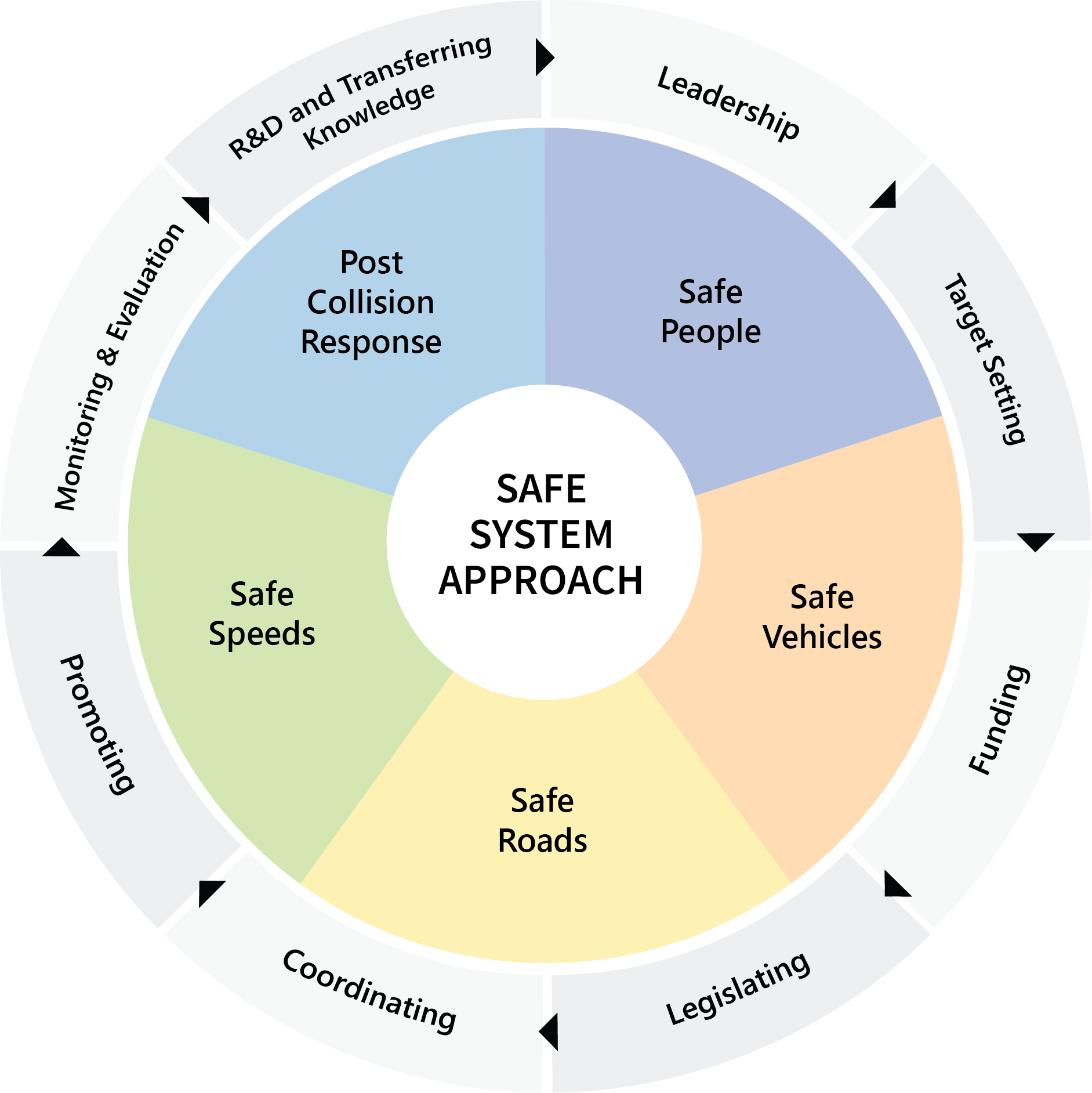
Key Elements of Road Safety Management
The following content highlights the core elements of effective road safety management. Each element is explained with a focus on its role in promoting safer road environments and fostering collaborative efforts to reduce risks and improve outcomes.
Leadership
With a focus on driving the road safety vision and ensuring accountability, leadership inspires collaboration across all stakeholders to achieve unified goals. Accompanied by an icon of a leader figure or lightbulb, this element symbolises the guiding force behind road safety strategies.
Target Setting
Target setting defines clear and measurable goals for improving safety. It ensures consistent progress tracking to reduce collisions and casualties effectively.
Funding
Funding secures the necessary resources to implement impactful safety initiatives. It ensures the sustainability of long-term strategies that address road safety challenges.
Legislating
Legislation defines the rules and frameworks required to create safer road environments. It is crucial for enforcing compliance and supporting the effective governance of road safety measures.
Coordinating
Coordination brings together stakeholders from various sectors to align their efforts and act in harmony. It maximises the effectiveness of road safety initiatives through collaboration.
Promoting
Promotion increases public awareness of road safety issues and encourages behavioural changes. It plays a vital role in fostering safer practices through educational campaigns and outreach.
Monitoring & Evaluation
Monitoring and evaluation involve assessing the performance of road safety measures through data-driven processes. By leveraging data, these efforts refine strategies and ensure continuous improvement in achieving safer road environments.
Research & Development (R&D) and Transferring Knowledge
Research and development focus on creating innovative solutions to emerging road safety challenges. Knowledge transfer ensures that effective practices are shared and applied across stakeholders to enhance overall safety.
The Implementation Gap:
Bridging the Outer Layer and the Core Principles
The implementation gap between the outer layer and the core principles of the Safe System Approach (Safe Roads, Safe Speeds, Safe Vehicles, Safe People, Post-Collision Response) is a critical challenge in achieving road safety objectives.
This gap can be effectively addressed through a model focusing on Commitment, Capacity, Capability, and Culture, which are further explained below:
The Safe System approach requires strong leadership, stakeholder ownership, and sufficient resources to achieve its goals effectively.
Delivery organisations must be able to operate at a sufficient scale to ensure impactful outcomes. The system is designed to encourage a proactive approach to road safety.
Agencies involved in delivery must have the necessary skills and expertise to implement the Safe System effectively. These capabilities should be supported by clear guidance and ongoing training.
A successful Safe System relies on a shared culture, built on agreed ambitions, common values, and a unified language that aligns all stakeholders toward the goal of reducing road harm.
Commitment: Leadership That Inspires Action
What is it?
Commitment means that leaders – from government officials to local policymakers – actively prioritise road safety, ensuring it becomes a shared goal for the entire community.
Why is it important?
Without strong leadership, road safety initiatives may lack the funding, direction, or urgency needed to succeed.
What does it look like?
- Setting clear, measurable goals to reduce deaths and injuries
- Allocating resources (like budgets and staff) to make road safety a reality
- Communicating the importance of road safety regularly and visibly.
Capacity: Equipping Organisations to Deliver Results
What is it?
Capacity refers to the resources, structures, and skills needed to implement effective road safety measures.
Why is it important?
Even the best ideas can fail without the right people, processes, and funding to carry them out.
What does it look like?
- Governments and organisations investing in skilled teams, tools, and infrastructure
- Creating long-term plans with funding to sustain road safety programs
- Offering training and education to road safety professionals.
Capability: Utilising Tools, Technology and Expertise
What is it?
Capability means having the right tools, technologies, and expertise to address road safety challenges effectively.
Why is it important?
Modern road safety relies on data and technology to identify risks and take action.
What does it look like?
- Using traffic management systems to monitor and improve road conditions
- Analysing crash data to understand why collisions happen and prevent them
- Partnering with researchers to develop solutions based on evidence and best practices.
Culture: Building a Community Where Safety Comes First
Commitment: Leadership That Inspires Action
What is it?
Commitment means that leaders – from government officials to local policymakers – actively prioritise road safety, ensuring it becomes a shared goal for the entire community.
Why is it important?
Without strong leadership, road safety initiatives may lack the funding, direction, or urgency needed to succeed.
What does it look like?
- Setting clear, measurable goals to reduce deaths and injuries
- Allocating resources (like budgets and staff) to make road safety a reality
- Communicating the importance of road safety regularly and visibly.
Capacity: Equipping Organisations to Deliver Results
What is it?
Capacity refers to the resources, structures, and skills needed to implement effective road safety measures.
Why is it important?
Even the best ideas can fail without the right people, processes, and funding to carry them out.
What does it look like?
- Governments and organisations investing in skilled teams, tools, and infrastructure
- Creating long-term plans with funding to sustain road safety programs
- Offering training and education to road safety professionals.
Capability: Utilising Tools, Technology and Expertise
What is it?
Capability means having the right tools, technologies, and expertise to address road safety challenges effectively.
Why is it important?
Modern road safety relies on data and technology to identify risks and take action.
What does it look like?
- Using traffic management systems to monitor and improve road conditions
- Analysing crash data to understand why collisions happen and prevent them
- Partnering with researchers to develop solutions based on evidence and best practices.
What is it?
A safety culture means that road safety becomes a part of everyday life, where everyone – drivers, cyclists, pedestrians, and policymakers – values and promotes safe behaviours.
Why is it important?
Lasting change happens when individuals and communities take ownership of road safety.
What does it look like?
- Public awareness campaigns that teach people how to stay safe on the roads
- Education programs for drivers, cyclists, and children
- Recognising and celebrating people who make road safety a priority.
Culture: Building a Community Where Safety Comes First
What is it?
A safety culture means that road safety becomes a part of everyday life, where everyone – drivers, cyclists, pedestrians, and policymakers – values and promotes safe behaviours.
Why is it important?
Lasting change happens when individuals and communities take ownership of road safety.
What does it look like?
- Public awareness campaigns that teach people how to stay safe on the roads
- Education programs for drivers, cyclists, and children
- Recognising and celebrating people who make road safety a priority.
